The Psychology Behind Successful Stock Market Investing
Investing in the stock market often seems like a game of numbers and strategies, but a critical yet sometimes overlooked factor is psychology. Emotions, biases, and mental habits can all significantly impact an investor's decisions and outcomes. Understanding the psychology behind successful investing is just as important as understanding the market mechanics. This article will examine the mental factors influencing stock market behaviour and how investors can use psychological insights to improve their strategies and avoid common pitfalls.
The Role Of Emotions In Stock Market Investing
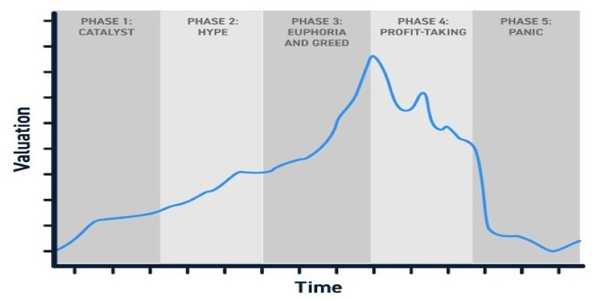
One of the most significant psychological factors in investing is emotion. Fear and greed are two emotions that heavily influence stock market behaviour. Fear can lead investors to panic during market downturns, selling off stocks at a loss to protect themselves from further losses. On the other hand, greed can drive investors to chase high returns during bull markets, making rash decisions without fully considering the risks.

Fear of losing money can cause investors to hesitate, avoid taking risks, or even exit the market prematurely. This often leads to missed opportunities. For instance, an investor might sell off stocks during a market dip, only to watch them rebound in value shortly after. Such reactions are typically fueled by short-term thinking and a lack of patience.
Greed, meanwhile, is often the driving force behind irrational exuberance. During periods of market growth, many investors are drawn to the promise of high returns and can become overconfident in their ability to predict market movements. This overconfidence can lead them to invest in speculative stocks or take on more risk than they can handle. When the market corrects, these investors may suffer significant losses due to overextended positions.
Cognitive Biases And Their Impact On Decision-Making
Cognitive biases are another crucial psychological factor that affects investing. These are mental shortcuts that people use to make decisions quickly, but they often lead to errors in judgment. Several cognitive biases commonly influence stock market behaviour, including confirmation bias, loss aversion, and the anchoring effect.
Confirmation bias is the tendency to seek information that supports existing beliefs or opinions while disregarding information that contradicts them. In the context of investing, this can lead an investor to focus only on positive news about a particular stock while ignoring red flags. For example, an investor bullish on a stock may selectively read reports or news articles that align with their view, reinforcing their confidence in the stock, even when other data suggest caution.
Loss aversion is the idea that people experience the pain of loss more intensely than the pleasure of a comparable gain. In investing, this can manifest in an unwillingness to sell a losing stock, hoping that it will eventually rebound. Investors might hold on to losing investments for far too long, unwilling to accept the reality that the stock may never recover, which can tie up capital that could be better invested elsewhere.
The anchoring effect occurs when investors fixate on a specific reference point, such as a stock's historical price or past performance, and use it as a basis for future expectations. This can lead to faulty decision-making, as investors might assume that a stock will always return to its previous high without considering changes in the market environment or the company's fundamentals.
The Importance Of Patience And Long-Term Thinking
Patience is a critical psychological trait for successful investing. The stock market can be volatile, with sharp fluctuations in price over short periods. Investors who lack patience may be tempted to react impulsively to market movements, leading them to make hasty decisions that could harm their portfolios.

Long-term thinking is crucial in the stock market because, over time, the market tends to trend upwards despite short-term volatility. Historically, equity markets have provided substantial returns to investors who can stay invested for the long haul. However, many investors struggle with short-term thinking, often wanting immediate investment results.
Successful investors understand that wealth-building through stocks is typically a slow and steady process. They focus on the fundamentals of the companies they invest in rather than reacting to market noise or trying to time the market. By sticking to a long-term plan and maintaining discipline, these investors can ride out market fluctuations and ultimately benefit from the market's upward trajectory.
Behavioural Traps And How To Avoid Them
Even seasoned investors can fall victim to behavioural traps. These traps often stem from emotional responses or biases and can lead to poor investment choices. Understanding these traps and how to avoid them is crucial for anyone looking to succeed in the stock market.

Herd mentality is one of the most common behavioural traps. This occurs when investors follow the crowd, buying stocks because everyone else is buying without conducting their research. Herd mentality can drive up stock prices artificially, creating bubbles that eventually burst. Successful investors avoid this trap by making decisions based on their analysis rather than following the crowd.
Another trap is overconfidence bias, where investors believe they have superior knowledge or insight into the market, leading them to take on excessive risk. Overconfident investors may ignore warning signs or make decisions without fully understanding the potential consequences. To avoid this, successful investors recognize the limits of their knowledge and take a conservative, well-researched approach to investing.
Mindfulness And Emotional Control In Investing
Mindfulness, or being fully present and aware of one's thoughts and emotions, can be a powerful tool for investors. By practising mindfulness, investors can better control their emotional reactions to market fluctuations, making it easier to stay calm and rational during periods of high volatility.

Emotional control is essential for maintaining a long-term perspective and avoiding impulsive decisions. Many successful investors use mindfulness techniques like meditation or journaling to help manage Stress and stay focused on their investment goals. By taking the time to pause and reflect before making decisions, they can ensure that their actions are based on careful analysis rather than emotional impulses.
Conclusion
Successful stock market investing requires more than just financial knowledge and technical skills. The psychology behind investing plays a significant role in determining an investor's success. Emotions, cognitive biases, and mental habits can all impact investment decisions, either positively or negatively. Investors can improve their chances of long-term success by understanding these psychological factors and taking a disciplined, patient, and data-driven approach to investing.
Managing emotions, overcoming cognitive biases, practising patience, and avoiding behavioural traps are all crucial steps in developing a successful investment strategy. By cultivating mindfulness and emotional control, investors can stay focused on their long-term goals and make better decisions, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes in the stock market.